Genetic polymorphism in ATG16L1 gene influences the response to adalimumab in Crohn's disease patients | Pharmacogenomics

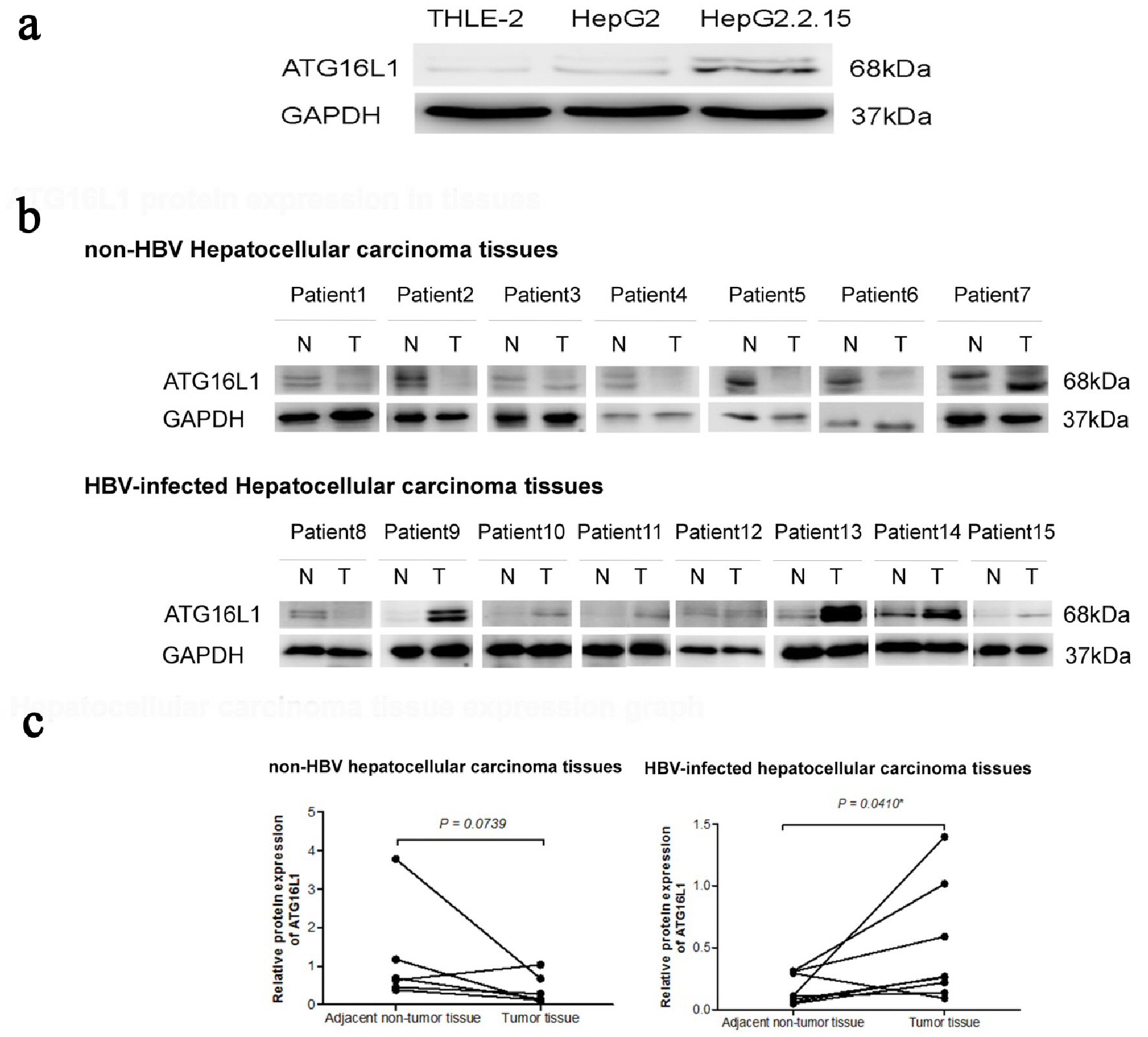
Non‐canonical autophagy functions of ATG16L1 in epithelial cells limit lethal infection by influenza A virus | The EMBO Journal

Intrinsic lipid binding activity of ATG16L1 supports efficient membrane anchoring and autophagy | The EMBO Journal
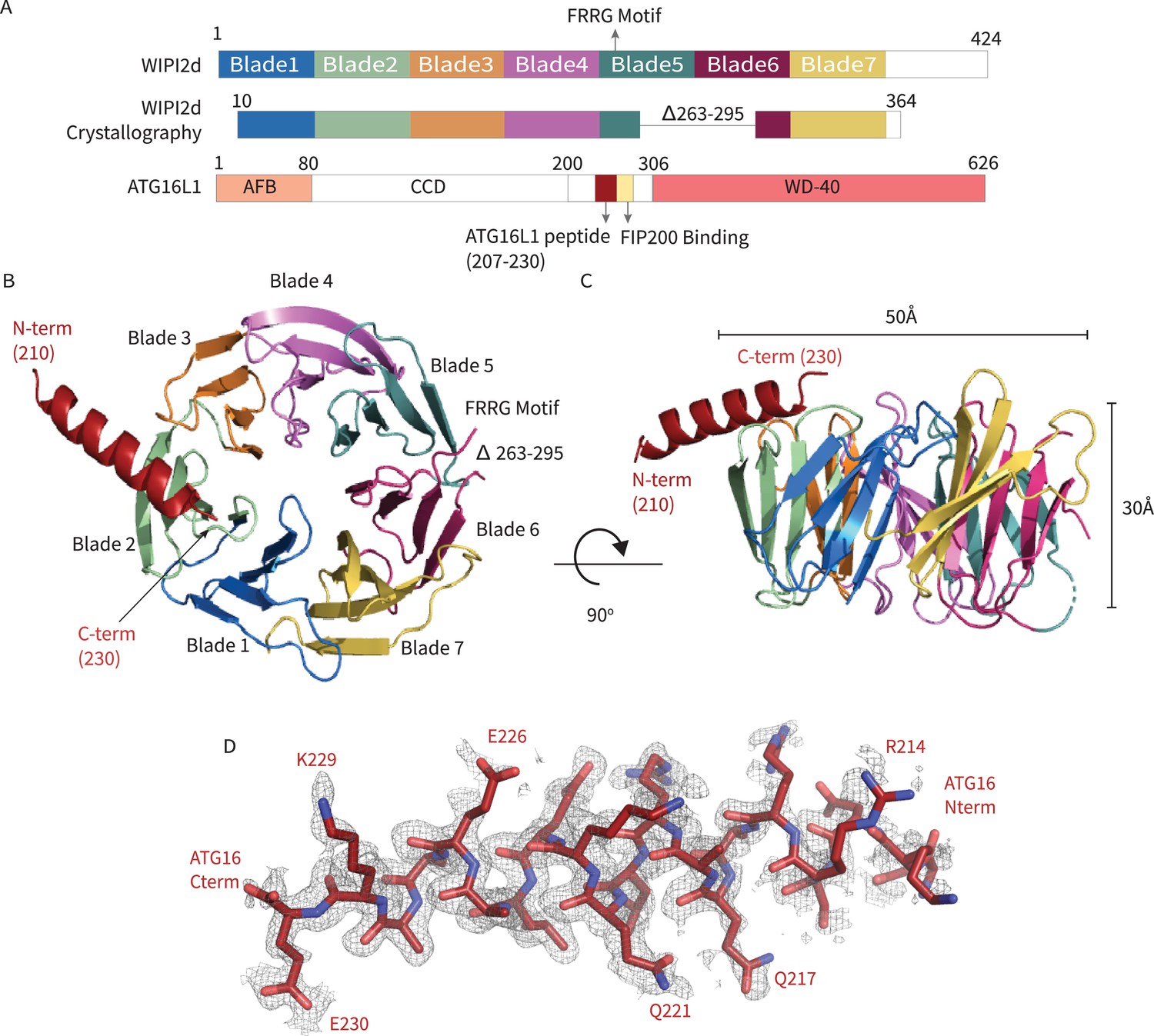
The N-Terminal Region of the Human Autophagy Protein ATG16L1 Contains a Domain That Folds into a Helical Structure Consistent with Formation of a Coiled-Coil | PLOS ONE

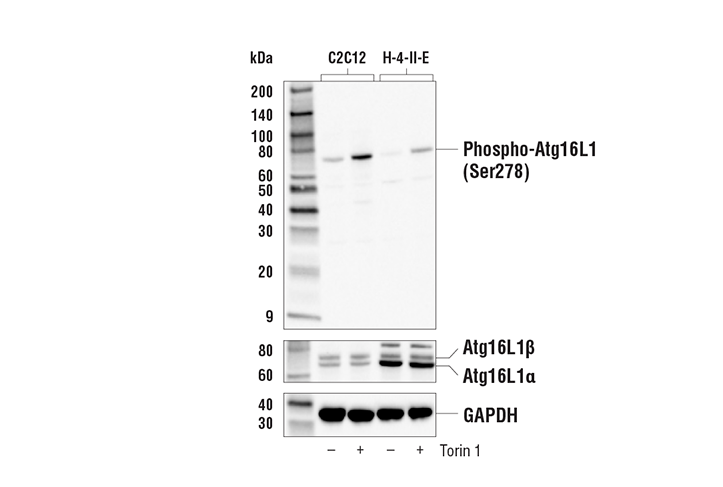
ULK1‐mediated phosphorylation of ATG16L1 promotes xenophagy, but destabilizes the ATG16L1 Crohn's mutant | EMBO reports
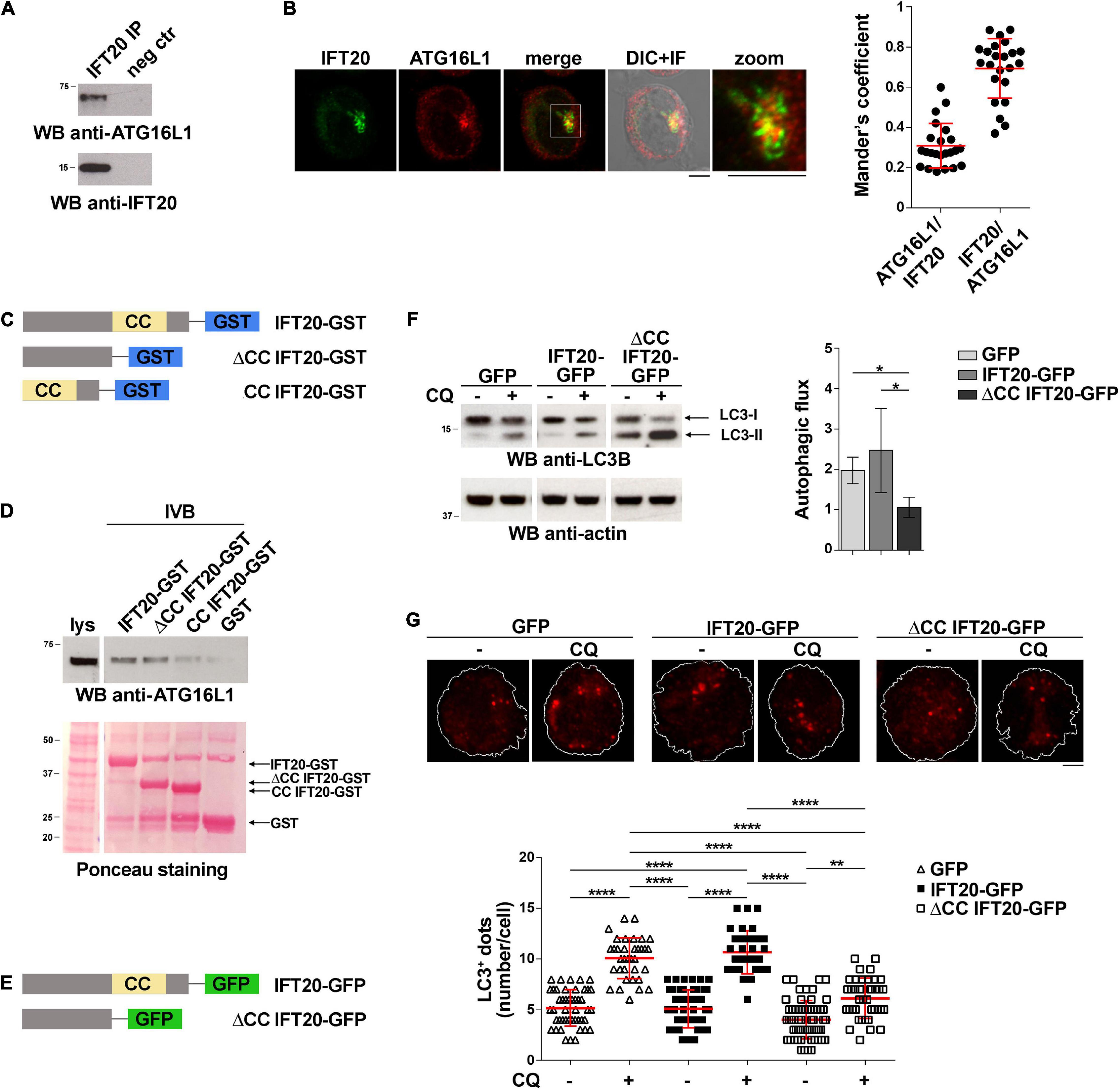
Frontiers | The Intraflagellar Transport Protein IFT20 Recruits ATG16L1 to Early Endosomes to Promote Autophagosome Formation in T Cells

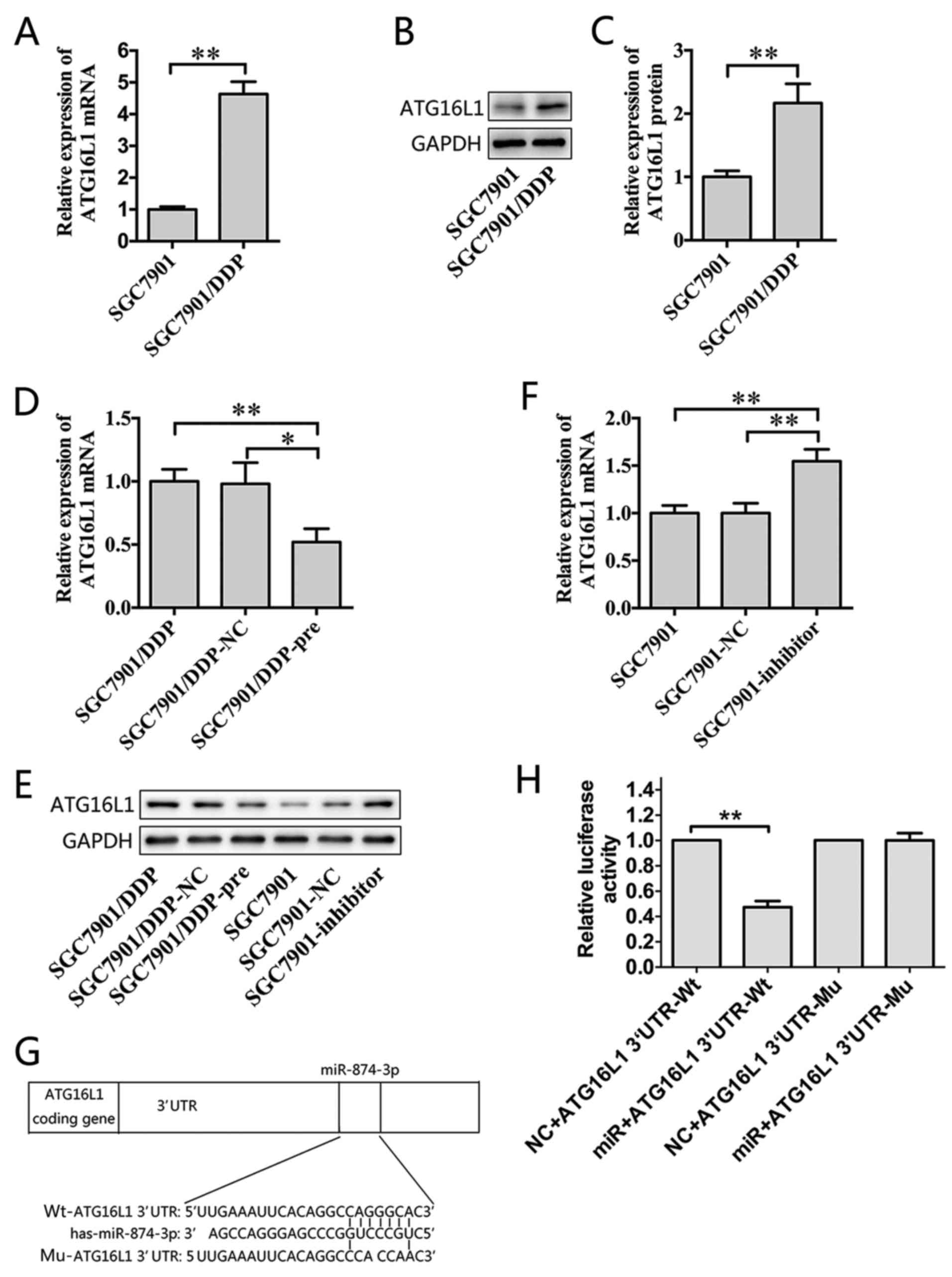
Association between ATG16L1 gene polymorphism and the risk of Crohn's disease - Bei-Bei Zhang, Yu Liang, Bo Yang, Ying-Jun Tan, 2017

Genes | Free Full-Text | The Association of ATG16L1 Variations with Clinical Phenotypes of Adult-Onset Still's Disease